Did you know that wound dehiscence after abdominal surgery is associated with mortality rates ranging from 10% to 44%? This serious postoperative complication involves the breakdown of a surgical incision site, potentially leading to extended hospital stays, additional surgeries, and significant patient discomfort.
Despite advancements in surgical techniques and wound healing protocols, wound dehiscence remains a concern for both patients and healthcare providers. Proper preoperative assessment, intraoperative precision, and diligent postoperative care are essential to minimize risks and promote optimal healing.
Risk Factors for Wound Dehiscence:
Patients older than 65 years are more likely to develop wound dehiscence because of deterioration in tissue repair mechanism compared with younger patients.
- Hypoproteinemia
- local wound infection
- anemia
- hypertension
- emergency surgery
- abdominal distension
- excessive coughing
- vomiting
- constipation
- nutrition status
- operative time exceeding 2.5 hours
- suture material, drain
- medical history such as obesity with body mass index (BMI) greater than 30
- stroke
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia
- malignancy
Pre-operative risk factors:
- poor laboratory findings
- infection
- hypertension
- emergency surgery
Wound infection is the most relevant factor, and it increases the possibility of wound dehiscence by decreasing tensile strength and fibroblast concentration. Decreased fibroblast concentration triggers tissue destruction during wound healing.
Hypoproteinemia also reduces tensile strength. It is required to reduce the incidence of wound dehiscence through preoperative control of these areas.
Postoperative risk factors include:
- abdominal distension
- excessive coughing
- vomiting
- constipation
- resolving these symptoms with appropriate medication may reduce the likelihood of wound dehiscence
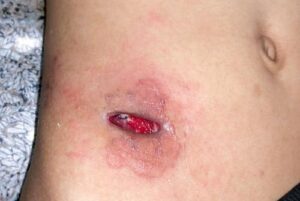
Treatment of Dehisced Surgical Wounds
A normal, healing surgical incision should be treated according to post-operative instructions, maintaining good hygiene, and using an appropriate dressing. Avoid unnecessary strain on the wound site. For a dehisced wound, a patient should return for wound care immediately. This may include wound debridement, antibiotic therapy, advanced wound healing products like cultured skin grafts, or the use of another type of wound closure device like a wound vac. Following this treatment, the wound will need to be monitored extremely closely for signs of recurring dehiscence.
At Vayu Advanced Wound Clinic, with Dr. Badam’s expertise in post-surgical wound care, she does a comprehensive exam, customizing wound care based on individual patients’ needs with a goal of “Quick wound healing”.
For a consultation with Dr. Badam, call or text 210-651-1112.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the early signs of wound dehiscence?
A: Symptoms include increased pain, redness, swelling, drainage of fluid or pus, and a visible opening of the wound. If you notice these, seek medical attention immediately.
Q: How can I reduce my risk of wound dehiscence after surgery?
A: Follow your surgeon’s post-operative care instructions, maintain a healthy diet, manage underlying health conditions, avoid heavy lifting, and monitor for signs of infection.
Q: Can wound dehiscence heal on its own?
A: Minor cases may heal with proper wound care, but severe dehiscence often requires medical intervention, including debridement, antibiotics, or surgical closure.
Q: When should I contact a doctor about my surgical wound?
A: If you experience excessive pain, persistent redness, unusual discharge, fever, or wound reopening, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Q: What role does nutrition play in wound healing?
A: Proper nutrition, especially protein intake, is crucial for tissue repair. Malnutrition, particularly hypoproteinemia, increases the risk of wound breakdown.
If you have concerns about your surgical wound, schedule an appointment with Dr. Badam at Vayu Advanced Wound Clinic today.